Antimicrobial drugs
are highly used to control diseases as it has to meet the world’s demand of
milk, meat, milk-by product, meat-by product, wool and other animal by products,
even more for providing adequate amountsto thegrowing world population. Medication
improve weightgain, feed efficiency and cure the diseases infood producing
animals. However, the productivity in terms of quality can not be obtain as
there is a risk associated withresidues that remain in the tissues of treated
animals at the timeof slaughter or residues in animal derived products like meat,
milk,eggs and honey that poses a health hazard to the consumer. There are many
factors influencing the occurrence of residuesin animal products such as drug’s
properties and theirpharmacokinetic and dynamic characteristics, drug vehicle, physicochemical
or biologicalreactions of animal body and processes on animal products.The most
common reason are improper usage, extra-label or illegaldrug
applications.People who are working in food industries and medical concern have
drawn public attention to the threat of pesticides in the environment and in
food. Use of diethylstilbestrol (DES), growth promoters, mal-injection of
oxytocin, use of bovine somatotropin, pesticide added fodders for animal
consumption are few examples of residual impact on consumers.
Antimicrobial residues in animal and its food product majorly leads to the antimicrobial drug resistant and it impact on the global health.
Antimicrobial residues in animal and its food product majorly leads to the antimicrobial drug resistant and it impact on the global health.
Factors affecting drug residues
It is one of the major problems for food contamination.
1)
Not
following the recommended label instructions.
2)
Not following
of recommended withdrawal times when antibiotic used.
3)
Administering
too large volume at a single injection site may extend the drug release and
metabolic time.
4)
Used to
mix multiple drugs.
5)
Dosing,
measuring, or mixing errors; allowing animals access to spilled chemicals or
medicated feeds Animal effects- age, pregnancy, congenital, illness, allergies
kind of animal factors.
6)
Chemical
interactions between multiple drugs.
7)
Environmental
contamination may alter.
8)
Improper
use of agricultural chemicals such as pesticides, plant growth promoters which
ultimately come into animal feed and then to the human.
Animal factors
a) Age and species
of animal:
Weaning status and
the age of the animal affect drug disposition. There is a probabiliy of species
variation among animals in theirl ability to excrete drugs in the bile; example,
chicken are good biliary excretes, whereas sheep and rabbit are characterized
as moderate and poor excretes.
b) Disease status
animal:
The disease
perspective of an animal can also affect the pharmacokinetics of drugs which
have administered, even it can influence the potential for residues. This can occur
either when the disease affects the metabolic system (and consequently drug
metabolism), or when the presence of infection and/or inflammation causes the
drug to accumulate in affected tissues.
Extra-label drug use (ELU)
Extra-label Drug Use
(ELU) refers to the use of an approved drug in a manner that is not in
accordance with the approved label directions.ELU happen, when human practice
drug used for animal.When a drug approved for one species of animal is used in another.When
a drug is used to treat a condition for which it was not approved. The use of
drugs at levels in excess of recommended dosages.Theuse of enrofloxacin
solution as a topical ear medication (only approved for use as an injection)
are the common ELU in veterinary medicine.
Improper withdrawal time
It is theinterval
required from the time of drug administration to the required duration of time
to excrete residues for safe food production before its slaughter. The
withdrawal time (clearance period) is the time for the residue of drugs to reach
at safe concentration as defined by the tolerance. Depending on the drug
product, dosage form and route ofadministration, the withdrawal time may vary
from a few hours to several days or weeks. Even different drugs have different
biological and excretion activity that hampered the standard drug withdrawal
time. Hence, improper withdrawal time is one the major concern for the presence
of drug residue in animal food.
Effects of veterinary drug residues on public
health
The major public
health effects of drug residue are development of antimicrobial drug
resistance, hypersensitivity reaction, carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, teratogenicity,
Infertility, disability and disruption of intestinal normal flora. Ideally, the
food product should not be consider for consumption until and unless there is
complete elimination of residues. However, it can not be possible to determine.
Hence, advancement of analytical equipment residues are denote as per the
amounts present like parts per million (ppm), parts per billion (ppb) and parts
per trillion (ppt) concentration.
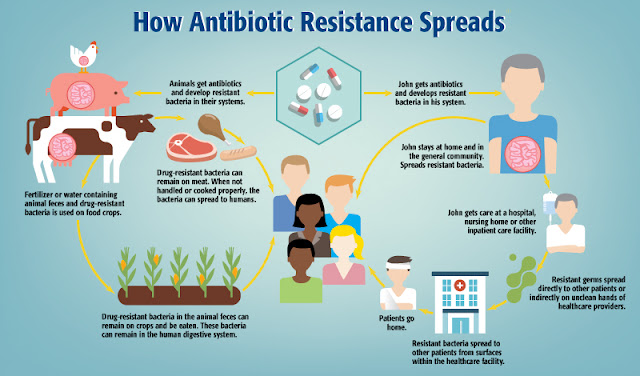
Development of drug resistance
Resistant
microorganism can come in contact easily to human, either through direct contact or indirectly
via milk, meat,egg and other by products. The use of antibiotic in livestock
production has direct relation with the development of human antibiotic resistance.
The animal fed with the lowprophylactic level of antibiotic may develop
bacteria evolving resistance to this antibiotic during the preparation or consumption
of food of animal origin. Human being obtains drug resistant bacteria such as
Salmonella, Campylobacter, and Staphylococcus from food of animal origin. This
is the major health concern. One cannot avoid food for survival, similarly one
cannot avoid of getting bacteria by inhalation, ingestion or by contact. Hence,
resistance is spreading very rapidly.
Drug hypersensitivity reaction
Allergic reactions
to drugs may include anaphylaxis, serum sickness, cutaneous reaction, a delayed
hypersensitivity response to drugs appear to be more commonly associated with the
antibiotics, especially of penicillin (About 10% of the human population is
hypersensitive), but in animals the extent of hypersensitive to the drug is not
well known. Certain macrolides may also be responsible for liver injuries,
caused by a specific allergic response to macrolide which hampered the hepatic
cells.
Carcinogenic effect
The potential
hazard of carcinogenic residues is relatedto their interaction or covalently binding
to various intracellular components such as proteins, deoxyribonucleic acid
(DNA), ribonucleic acid (RNA), glycogen, phospholipids, and glutathione.
Mutagenic effect
Several chemicals, including
alkalizing agents and analogous of DNA bases, have been shown to elicit potenicial
mutagenic activity. It has a potential hazard to the human population by
production of gene mutagen or chromosome breakage that may have adversely
affects human fertility.
Teratogenic effect
There are several
drugs which are contraindicated in pregnancy like Benzimidazole is embryo toxic
and teratogenic when given during early stage of pregnancy because of the anthelminthic
activity of the drug. In addition to embryo toxicity including teratogenicity,
the oxfendazole has also exhibited a mutagenic effect. When these drugs
administered to the cow and without allowing its clearance time, if pregnant
woman drink that cow’s milk, there is a more chances of occurrence of
teratogenicity.
Safety evaluation for veterinary drug
Residues Acceptable daily intake (ADI)
It is the amount of
a substance that can be ingesteddaily over a lifetime without appreciable
health risk. Calculation of ADI is based on an array of toxicological safety evaluation
takes into acute and long-term exposure of the drug and its potential impact.
Maximum residue limit (MRL)
It is defined as
the maximum concentration of any residue, resulting from the registered use of an
agricultural or veterinary chemical, which is recommended to be legally
permitted or recognized as acceptable in or on a food, agricultural commodity,
or animal feed. The concentration is expressed in milligrams per kilogram of
thecommodity (or milligrams per liter the case of a liquid commodity).
Detection methods
There
are different methods to detect drug residues like, liver enzyme digestion
test, identification of chemical bond and structure of chemical, Tissue
extraction methods, Analytical methods, Gas liquid chromatography (GLC), HPLC,
Fluorescence analysis method, Marker residue detection method.
Measure to prevent residues
Most
pharmacokinetic parameters have been determined in healthy animals. Yet
diseased animals might have altered physiology. This may result in increased elimination
a half-life by a factor of six or more or less. Doubling dose of the drug
should only prolong the approved withdrawal time by one half-life; however,
doubling the half-life as a result of the disease might do the double the
necessary withdrawal time pathophysiologic states. Hence, It must be required
intensive study on diseased model of animal.
The residue can be prevented by following
measures:
- Farm herd management must be follow. All food animals should be maintained in a clean and healthy environment and clean milk production strategy must be follow.
- Must give attention to withdrawal times, advice to farmer for withdrawal.
- Carefully read all instruction and then only administer the drug properly.
- VeterinaryAyurveda and homeopathic approach may helpful.
- Ethno-veterinary practices may be recommended and promoted to practice.
- Development of simple and economic field test to identify drug residues in edible animal products should required.
- Rapid screening procedures for the analysis of antibiotic residues and instant grading and prohibition of food containing antibiotics must be follow.
- Make individuals and organizations aware of the problem through education by veterinary personnel, organizations, and literatures and governmental agencies.
- Prevent careless use of pesticides and insecticides, as well as cleansing and sanitizing agents.
- Do not give overdose from recommended levels and do not combine several antibiotics.
- Keep record of all treatments, including date of treatment, diagnosis, dosage of treatment.
- Keep record of treated animals.
- Prevent extra-label drug use.
Conclusion
Use of antimicrobial drugs in food-producing
animals have the risk factor to retain their residues in animal, by product and
their derived products. Which is the health hazard to the consumers. The most
prone reason for this, are improper management in treatments, improper usage,
overdose, use of long acting medication and failure by farmers to withdraw the
milk for the particular time period. As the pharma giants are launching their
newer products day by day, there is limited information particularly veterinary
drug residue. Therefore, research area should be focus to generate data
regarding the residual time- period. Strict withdrawal time should be
practiced. Farmers and Veterinarian can be trained as a step guard to prevent the
residue hazards.

Post a Comment